Sperm health
Sperm motility
The level of sperm motility is an important factor for the efficient movement in the female reproductive tract. When sperm cells are not fast enough, they die off before they reach the egg.
Motility is divided into three categories:
Motility is classified as normal if more than 32% of the sperm are progressive.
Sperm concentration
Sperm concentration or sperm count provide prognostic and diagnostic information: It shows the amount of sperm released during sexual intercourse. This allows the determination of sperm production, sperm reserves in the epididymis as well as the patency of the sperm duct system.
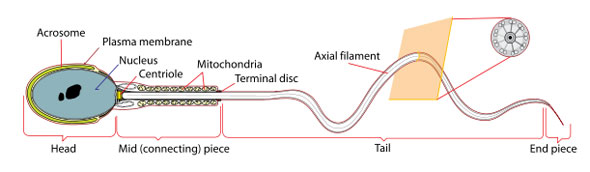
Sectional view
Morphology (shape)
The appearance of the sperm is crucial for the assessment of fertility. Various criteria are used to assess human sperm morphology with different classification systems for head, mid-piece and tail defects identified under the microscope.
Morphology is classified as normal, if the average number of sperm with a normal shape is 4% or more.
Vitality
Sperm vitality is the percentage of sperm in the ejaculate that are alive.